The update provides clarity on how to apply the Alice/Mayo test to AI innovations and includes examples of how the test applies in concrete cases.
United States
Intellectual Property
To print this article, all you need is to be registered or login on Mondaq.com.
On July 17th, the USPTO issued a guidance update to
help USPTO personnel and those who interact with the agency
evaluate the subject matter eligibility of claims in patent
applications involving artificial intelligence (AI). It walks
through the well-documented Alice/Mayo test and adds certain
details about using it to evaluate AI-related claims.
The update (
“2024 Guidance Update on Patent Subject Matter Eligibility,
Including on Artificial Intelligence”) was released in
accordance with President Biden’s Executive Order 14110, which
outlined the federal government’s suggested approaches and
programs for the development and use of AI.
The USPTO also issued a set of
“Subject Matter Eligibility Examples,” which gives
concrete examples of claims and how each should be assessed in
light of the update. It considers three examples:
- Anomaly Detection: Includes claims directed at the use of
neural networks to detect malicious network packets, and
specifically, the use of AI-based methods to enhance the
functionality of the models over time. - Speech Separation: Includes claims directed to identifying and
separating extraneous or background speech from speech signals for
further analysis and processing, and how AI can be used to refine
operations or generate novel solutions. - Fibrosis Treatment: Includes methods for using AI models to
create personalized treatments for fibrosis patients, and how AI
can provide new ways for users to interact with systems or
applications.
The document includes a chart, reproduced below, that summarizes
how each example meets or does not meet criteria in the Alice/Mayo
test.
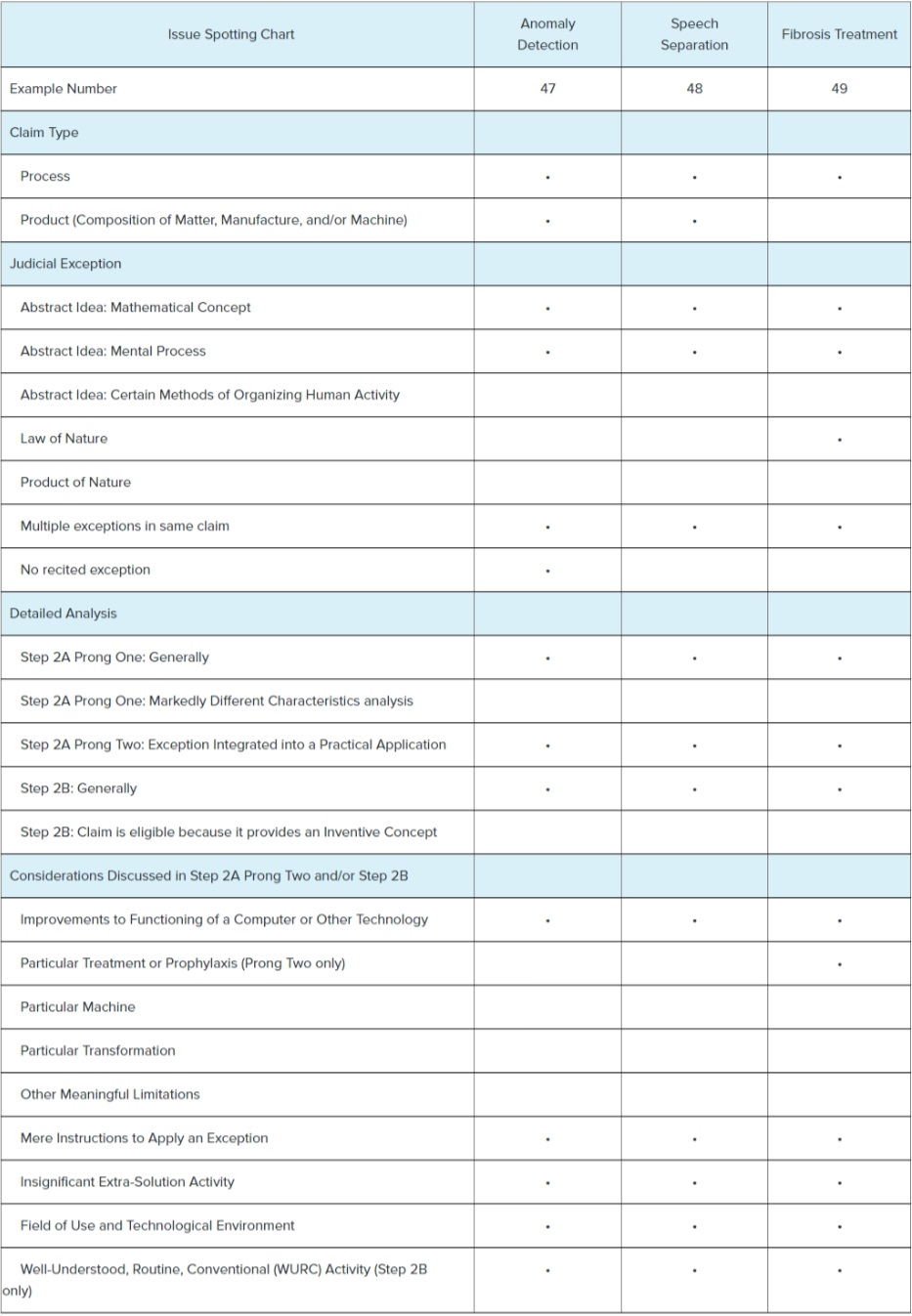
In the anomaly detection example, the USPTO highlights
considerations such as whether the invention improves the
algorithm’s performance (e.g., enable it to get better at
identifying malware over time or use less processing resources to
achieve the same result) and how the use of the algorithm achieves
a specific, practical benefit (such as enabling a network to become
safer or more secure, or recommending remediation actions).
In the speech separation example, considerations that impact
patentability include how AI is applied to optimize industrial or
business processes and the extent to which those optimizations
solve problems more effectively than existing methods.
In the fibrosis treatment example, the guide describes how AI
technologies can be applied to enhance user interactions (such as
AI-driven chatbots or adaptive interfaces) that personalize user
experience based on behavior and preferences. In these cases, the
application should focus on the innovative aspects of the user
interface that are enhanced or enabled by AI, and the novel ways in
which the interface adapts to user inputs or preferences. Specifics
include the use of natural language processing, pattern
recognition, or adaptive learning systems.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general
guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought
about your specific circumstances.








