In terms of absolute levels of intangible investments for 2020 (latest year for which data is available), India ranks 14th among a sample of 26 advanced economies, trailing Denmark and ahead of Finland and Portugal, the World Intangible Investment Report said.
Overall, the data underscores India’s significant progress and growing importance in the global arena of intangible assets, reflecting its expanding role in innovation and intellectual property. The data assumes significance because this is the first time ever the intangible investment insights are available for India.
Simply put, intangible assets encompass R&D, know-how, software and data, design, brands and reputation — all assets that either result from or interact with intellectual property (IP) in some form. Despite their intangible nature, such assets have the power to create immense value for companies, economies and societies, industry experts told TOI.
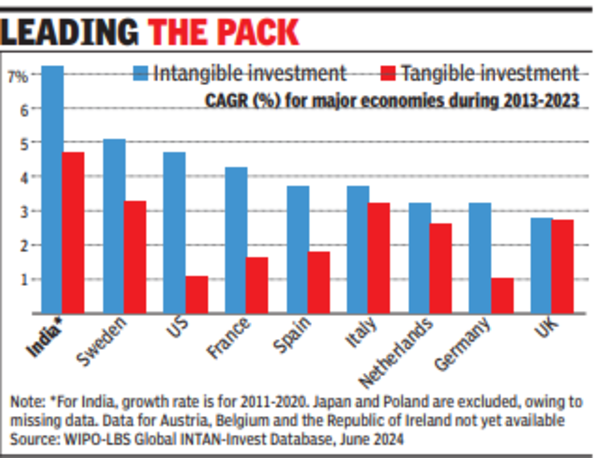
Further, the most noteworthy finding from the report is that India’s performance rivals that of high-income countries, such as Germany and Japan, in terms of intangible investment intensity (as a share of GDP).
“India showed the fastest growth in intangible investment, surpassing the growth rates of many developed economies, mainly driven by its strength in software and data,” Sacha Wunsch-Vincent, head, department of economics and data analytics at WIPO (World Intellectual Property Organisation) and one of the authors of the report, told TOI.
The biggest driver for India’s growth in intangible assets are software and data, new financial products and increasing investment in domestic brands.
Excluding the informal sector, intangible investment in 2019 made up over 10% of India’s GDP, which is comparable to EU-22 average (about 10%) and higher than Japan (about 9%). As a result, India’s intangible investment intensity is considerably higher than what would be expected relative to its level of development, an industry expert said.







